Art of Assembly/Win32 Edition is now available. Let me read that version.
PLEASE: Before emailing me asking how to get a hard copy of this text, read this.
Important Notice: As you have probably discovered by now, I am no longer updating this document. The reason is quite simple: I'm working on a Windows version of "The Art of Assembly Language Programming". In the past I have encouraged individuals to send me corrections to this text. However, as I am no longer updating this material, don't expect those correctioins to appear in a future release. I am collecting errata that I will post to Webster someday, so feel free to continue sending corrections to AoA/DOS (16-bit) to rhyde@cs.ucr.edu. If you're more interested in leading edge material, please see the information about the Win/32 edition, above.

Rudder pedals are really nothing more than a specially designed game paddle designed so you can activate them with your feet. Many flight simulator games take advantage of this input device to provide a more realistic experience. Generally, you would use rudder pedals in addition to a joystick device.
A joystick contains two pots connected with a stick. Moving the joystick along the x-axis actuates one of the pots, moving the joystick along the y-axis actuates the other pot. By reading both pots, you can roughly determine the absolute position of the pot within its working range.

An RC simulator is really nothing more than a box containing two joysticks. The yoke and steering wheel devices are essentially the same device, sold specifically for flight simulators or automotive games. The steering wheel is connected to a pot that corresponds to the x-axis on the joystick. Pulling back (or pushing forward) on the wheel activates a second pot that corresponds to the y-axis on the joystick.
Certain joystick devices, generically known as flight sticks, contain three pots. Two pots are connected in a standard joystick fashion, the third is connected to a knob which many games use for the throttle control. Other joysticks, like the Thrustmaster' or CH Products' FlightStick Pro, include extra switches including a special "cooley switch" that provide additional inputs to the game. The cooley switch is, essentially, a digital pot mounted on the top of a joystick. Users can select one of four positions on the cooley switch using their thumb. Most flight simulator programs compatible with such devices use the cooley switch to select different views from the aircraft.


The four switches come in on the H.O. four bits of I/O port 201h. If the user is currently pressing a button, the corresponding bit position will contain a zero. If the button is up, the corresponding bit will contain a one.
The pot inputs might seem strange at first glance. After all, how can we represent one of a large number of potential pot positions (say, at least 256) with a single bit? Obviously we can't. However, the input bit on this port does not return any type of numeric value specifying the pot position. Instead, each of the four pot bits is connected to an input of a resistive sensitive 558 quad timer chip. When you trigger the timer chip, it produces an output pulse whose duration is proportional to the resistive input to the timer. The output of this timer chip appears as the input bit for a given pot. The schematic for this circuit is
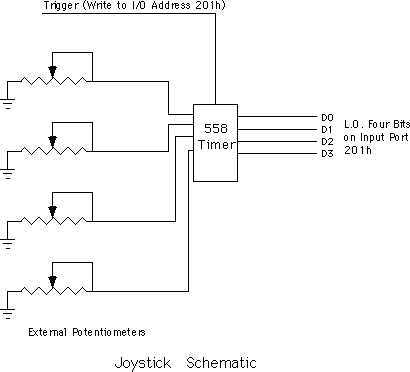
Normally, the pot input bits contain zero. When you trigger the timer chip, the pot input lines go high for some period of time determined by the current resistance of the potentiometer. By measuring how long this bit stays set, you can get a rough estimate of the resistance. To trigger the pots, simply write any value to I/O port 201h. The actual value you write is unimportant. The following timing diagram shows how the signal varies on each pot's input bit:

The only remaining question is "how do we determine the length of the pulse?" The following short loop demonstrates one way to determine the width of this timing pulse:
mov cx, -1 ;We're going to count backwards
mov dx, 201h ;Point at joystick port.
out dx, al ;Trigger the timer chip.
CntLp: in al, dx ;Read joystick port.
test al, 1 ;Check pot #0 input.
loopne CntLp ;Repeat while high.
neg cx ;Convert CX to a positive value.
When this loop finish execution, the cx register will contain the number of passes made through this loop while the timer output signal was a logic one. The larger the value in cx, the longer the pulse and, therefore, the greater the resistance of pot #0.
There are several minor problems with this code. First of all, the code will obviously produce different results on different machines running at different clock rates. For example, a 150 MHz Pentium system will execute this code much faster than a 5 MHz 8088 system. The second problem is that different joysticks and different game adapter cards produce radically different timing results. Even on the same system with the same adapter card and joystick, you may not always get consistent readings on different days. It turns out that the 558 is somewhat temperature sensitive and will produce slightly different readings as the temperature changes.
Unfortunately, there is no way to design a loop like the above so that it returns consistent readings across a wide variety of machines, potentiometers, and game adapter cards. Therefore, you have to write your application software so that it is insensitive to wide variances in the input values from the analog inputs. Fortunately, this is very easy to do, but more on that later.
mov cx, -1 ;We're going to count backwards
mov dx, 201h ;Point at joystick port.
out dx, al ;Trigger the timer chip.
CntLp: in al, dx ;Read joystick port.
test al, 1 ;Check pot #0 input.
loopne CntLp ;Repeat while high.
neg cx ;Convert CX to a positive value.
As mentioned earlier, the big problem with this code is that you are going to get wildly different ranges of values from different game adapter cards, input devices, and computer systems. Clearly you cannot count on the code above always producing a value in the range 0..180h under these conditions. Your software will need to dynamically adjust the values it uses depending on the system parameters.
You've probably played a game on the PC where the software asks you to calibrate the joystick before use. Calibration generally consists of moving the joystick handle to one corner (e.g., the upper-left corner), pressing a button or key and them moving the handle to the opposite corner (e.g., lower-right) and pressing a button again. Some systems even want you to move the joystick to the center position and press a button as well.
Software that does this is reading the minimum, maximum, and centered values from the joystick. Given at least the minimum and maximum values, you can easily scale any reading to any range you want. By reading the centered value as well, you can get slightly better results, especially on really inexpensive (cheap) joysticks. This process of scaling a reading to a certain range is known as normalization. By reading the minimum and maximum values from the user and normalizing every reading thereafter, you can write your programs assuming that the values always fall within a certain range, for example, 0..255. To normalize a reading is very easy, you simply use the following formula:
![]()
The MaximumReading and MinimumReading values are the minimum and maximum values read from the user at the beginning of your application. CurrentReading is the value just read from the game adapter. NormalValue is the upper bounds on the range to which you want to normalize the reading (e.g., 255), the lower bound is always zero.
To get better results, especially when using a joystick, you should obtain three readings during the calibration phase for each pot - a minimum value, a maximum value, and a centered value. To normalize a reading when you've got these three values, you would use one of the following formulae:
If the current reading is in the range minimum..center, use this formula:
![]()
If the current reading is in the range center..maximum, use this formula:
![]()
A large number of games on the market today jump through all kinds of hoops trying to coerce joystick readings into a reasonable range. It is surprising how few of them use that simple formula above. Some game designers might argue that the formulae above are overly complex and they are writing high performance games. This is nonsense. It takes two orders of magnitude more time to wait for the joystick to time out than it does to compute the above equations. So use them and make your programs easier to write.
Although normalizing your pot readings takes so little time it is always worthwhile, reading the analog inputs is a very expensive operation in terms of CPU cycles. Since the timer circuit produces relatively fixed time delays for a given resistance, you will waste even more CPU cycles on a fast machine than you do on a slow machine (although reading the pot takes about the same amount of real time on any machine). One sure fire way to waste a lot of time is to read several pots one at a time; for example, when reading pots zero and one to get a joystick reading, read pot zero first and then read pot one afterwards. It turns out that you can easily read both pots in parallel. By doing so, you can speed up reading the joystick by a factor of two. Consider the following code:
mov cx, 1000h ;Max times through loop
mov si, 0 ;We'll put readings in SI and
mov di, si ; di.
mov ax, si ;Set AH to zero.
mov dx, 201h ;Point at joystick port.
out dx, al ;Trigger the timer chip.
CntLp: in al, dx ;Read joystick port.
and al, 11b ;Strip unwanted bits.
jz Done
shr ax, 1 ;Put pot 0 value into carry.
adc si, 0 ;Bump pot 0 value if still active.
add di, ax ;Bump pot 1 value if pot 1 active.
loop CntLp ;Repeat while high.
and si, 0FFFh ;If time-out, force the register(s)
and di, 0FFFh ; containing 1000h to zero.
Done:
This code reads both pot zero and pot one at the same time. It works by looping while either pot is active. Each time through the loop, this code adds the pots' bit values to separate register that accumulator the result. When this loop terminates, si and di contain the readings for both pots zero and one.
Although this particular loop contains more instructions than the previous loop, it still takes the same amount of time to execute. Remember, the output pulses on the 558 timer determine how long this code takes to execute, the number of instructions in the loop contribute very little to the execution time. However, the time this loop takes to execute one iteration of the loop does effect the resolution of this joystick read routine. The faster the loop executes, the more iterations the loop will run during the same timing period and the finer will be the measurement. Generally, though, the resolution of the above code is much greater than the accuracy of the electronics and game input device, so this isn't much of a concern.
The code above demonstrates how to read two pots. It is very easy to extend this code to read three or four pots. An example of such a routine appears in the section on the SGDI device driver for the standard game adapter card.
The other game device input, the switches, would seem to be simple in comparison to the potentiometer inputs. As usual, things are not as easy as they would seem at first glance. The switch inputs have some problems of their own.
The first issue is keybounce. The switches on a typical joystick are probably an order of magnitude worse than the keys on the cheapest keyboard. Keybounce, and lots of it, is a fact you're going to have to deal with when reading joystick switches. In general, you shouldn't read the joystick switches more often than once every 10 msec. Many games read the switches on the 55 msec timer interrupt. For example, suppose your timer interrupt reads the switches and stores the result in a memory variable. The main application, when wanting to fire a weapon, checks the variable. If it's set, the main program clears the variable and fires the weapon. Fifty-five milliseconds later, the timer sets the button variable again and the main program will fire again the next time it checks the variable. Such a scheme will totally eliminate the problems with keybounce.
The technique above solves another problem with the switches: keeping track of when the button first goes down. Remember, when you read the switches, the bits that come back tell you that the switch is currently down. It does not tell you that the button was just pressed. You have to keep track of this yourself. One easy way to detect when a user first presses a button is to save the previous switch reading and compare it against the current reading. If they are different and the current reading indicates a switch depression, then this is a new switch down.
ah register with 84h and dx with an appropriate SGDI function code and then executing an int 15h instruction. The SGDI interface simply extends the functionality of the built-in BIOS routines. Note that and program that calls the standard BIOS joystick routines will work with an SGDI driver. The following table lists each of the SGDI functions:| DH | Inputs | Outputs | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 00 | dl = 0 |
al- Switch readings |
Read4Sw. This is the standard BIOS subfunction zero call. This reads the status of the first four switches and returns their values in the upper four bits of the al register. |
| 00 | dl = 1 |
ax- pot 0bx- pot 1cx- pot 2dx- pot 3 |
Read4Pots. Standard BIOS subfunction one call. Reads all four pots (concurrently) and returns their raw values in ax, bx, cx, and dx as per BIOS specifications. |
| 01 | dl = pot # |
al= pot reading |
ReadPot. This function reads a pot and returns a normalized reading in the range 0..255. |
| 02 | dl = 0al = pot mask |
al = pot 0ah = pot 1dl = pot 2dh = pot 3 |
Read4. This routine reads the four pots on the standard game adapter card just like the Read4Pots function above. However, this routine normalizes the four values to the range 0..255 and returns those values in al, ah, dl, and dh. On entry, the al register contains a "pot mask" that you can use to select which of the four pots this routine actually reads. |
| 03 | dl = pot # al = minimum bx= maximum cx= centered |
- | Calibrate. This function calibrates the pots for those calls that return normalized values. You must calibrate the pots before calling any such pot functions (ReadPot and Read4 above). The input values must be raw pot readings obtained by Read4Pots or other function that returns raw values. |
| 04 | dl = pot # |
al = 0 if not calibrated, 1 if calibrated. |
TestPotCalibrate. Checks to see if the specified pot has already been calibrated. Returns an appropriate value in al denoting the calibration status for the specified pot. See the note above about the need for calibration. |
| 05 | dl = pot # |
ax = raw value |
ReadRaw. Reads a raw value from the specified pot. You can use this call to get the raw values required by the calibrate routine, above. |
| 08 | dl= switch # |
ax = switch value |
ReadSw. Read the specified switch and returns zero (switch up) or one (switch down) in the ax register. |
| 09 | - | ax = switch values |
Read16Sw. This call lets an application read up to 16 switches on a game device at a time. Bit zero of ax corresponds to switch zero, bit 15 of ax corresponds to switch fifteen. |
| 80h | - | - | Remove. This function removes the driver from memory. Application programs generally won't make this call. |
| 81h | - | - | TestPresence. This routine returns zero in the ax register if an SGDI driver is present in memory. It returns ax's value unchanged otherwise (in particular, ah will still contain 84h). |
ah= 84h, dx = 0al register. Bit four corresponds to switch zero, bit five to switch one, bit six to switch two, and bit seven to switch three. One zero in each bit position denotes a depressed switch, a one bit corresponds to a switch in the up position. This call is provided for compatibility with the existing BIOS joystick routines. To read the joystick switches you should use the Read16Sw call described later in this document.
ah= 84h, dx = 1ax (x axis/pot 0), bx (y axis/pot 1), cx (pot 2), and dx (pot 3) registers. These are raw, uncalibrated, pot readings whose values will differ from machine to machine and vary depending upon the game I/O card in use. This call is provided for compatibility with the existing BIOS joystick routines. To read the pots you should use the ReadPot, Read4, or ReadRaw routines described in the next several sections.
ah=84h, dh=1, dl=Pot number.al register. This routine also sets ah to zero. Although the SGDI standard provides for up to 255 different pots, most adapters only support pots zero, one, two, and three. If you attempt to read any nonsupported pot this function returns zero in ax. Since the values are normalized, this call returns comparable values for a given game control setting regardless of machine, clock frequency, or game I/O card in use. For example, a reading of 128 corresponds (roughly) to the center setting on almost any machine. To properly produce normalized results, you must calibrate a given pot before making this call. See the CalibratePot routine for more details.
ah = 84h, al = pot mask, dx=0200hRead4Pots). However, it returns normalized values in al (x axis/pot 0), ah (y axis/pot 1), dl (pot 2), and dh (pot 3). Since this routine returns normalized values between zero and 255, you must calibrate the pots before calling this code. The al register contains a "pot mask" value. The L.O. four bits of al determine if this routine will actually read each pot. If bit zero, one, two, or three is one, then this function will read the corresponding pot; if the bits are zero, this routine will not read the corresponding pot and will return zero in the corresponding register.
ah=84h, dh=3, dl=pot #, al=minimum value, bx=maximum value, cx=centered value.ReadPot or Read4 routines, you need to calibrate that pot. If you read a pot without first calibrating it, the SGDI driver will return only zero for that pot reading. To calibrate a pot you will need to read raw values for the pot in a minimum position, maximum position, and a centered position. These must be raw pot readings. Use readings obtained by the Read4Pots routine. In theory, you need only calibrate a pot once after loading the SGDI driver. However, temperature fluctuations and analog circuitry drift may decalibrate a pot after considerable use. Therefore, you should recalibrate the pots you intend to read each time the user runs your application. Furthermore, you should give the user the option of recalibrating the pots at any time within your program.
ah= 84h, dh=4 , dl = pot #.ax denoting not calibrated or calibrated, respectively. You can use the call to see if the pots you intend to use have already been calibrated and you can skip the calibration phase. Please, however, note the comments about drift in the previous paragraph.
ah = 84h, dh = 5, dl = pot #ax. You can use this routine to obtain minimum, centered, and maximum values for use when calling the calibrate routine.
ah= 84h, dh = 8, dl = switch #ax if the switch is not depressed. It returns one if the switch is depressed. Note that this value is opposite the bit settings the Read4Sw function returns.
ah = 84h, dh = 9ax register with bit 0 corresponding to switch zero, bit one corresponding to switch one, etc. Ones denote switch depressed and zeros denote switches not depressed. Since the standard game adapter only supports four switches, only bits zero through three of al contain meaningful data (for those devices). All other bits will always contain zero. SGDI drivers for the CH Product's Flightstick Pro and Thrustmaster joysticks will return bits for the entire set of switches available on those devices.
ah= 84h, dh= 80hTestPresence routine (described next) to see if the driver was actually removed from memory by this call.
ah=84h, dh=81hax=0 and a pointer to an identification string in es:bx. If an SGDI driver is not present, this call will return ax unchanged.